network typologies
Network Topology - arrangement of internet where device supposed to be
two type of network topology:
1. Logical - how device appear to be connected to each other example; packet tracer.
2. Physical- actual interconnection with wire and cables(actual connected).
example; can be PC and PC, PC to switch
+ sending information is faster
+ no traffic
- cannot connect more device
- the cable broke will affect the others.
+not expensive because only use one cable
+easy to install another device
-if one PC is broke it will affect others, because of using 1 cable.
-there will be traffic if many hosts want to send information at the same time.
figure 3(star topology)
+no traffic because 1 nodes have it own connection
+if 1 damage, it will not affect the others
- time-consuming to install
-if the switch is broke, there will be no connection to the devices.
+faster sending message
+adding PC won't affect the network
-no privacy
-only one PC can send 1 data at a time
Two type of mesh:
1.full mesh: all device connected
2.partially mesh: not all device connected to each other
+one cable broken won't affect the others
+ many paths to pass the message
-hard to install
-expensive
+faster to send a message
+easy to set up other PC
-expensive to set up
-if the distribution layer is broken all the user cannot access the network.
two type of network topology:
1. Logical - how device appear to be connected to each other example; packet tracer.
2. Physical- actual interconnection with wire and cables(actual connected).
point-to-point:
two device directly connected together
figure 1(point to point topologies)
example; can be PC and PC, PC to switch
+ sending information is faster
+ no traffic
- cannot connect more device
- the cable broke will affect the others.
BUS
use (1 backbone) 1 cable connected to several devices (it can be PC, Printer, laptop)
figure 2(BUS topology)
+easy to install another device
-if one PC is broke it will affect others, because of using 1 cable.
-there will be traffic if many hosts want to send information at the same time.
STAR
it uses a switch, hub or a router in the middle to connect to any devicefigure 3(star topology)
+no traffic because 1 nodes have it own connection
+if 1 damage, it will not affect the others
- time-consuming to install
-if the switch is broke, there will be no connection to the devices.
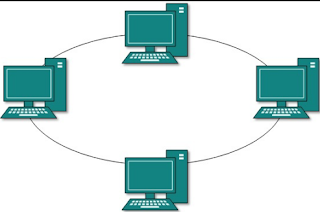
RING
directly connected to each other, in a form of a circle
figure 4 (ring topology)
+faster sending message
+adding PC won't affect the network
-no privacy
-only one PC can send 1 data at a time
MESH
the host connect to multiple hosts
figure 5(mesh topology)
Two type of mesh:
1.full mesh: all device connected
2.partially mesh: not all device connected to each other
+one cable broken won't affect the others
+ many paths to pass the message
-hard to install
-expensive
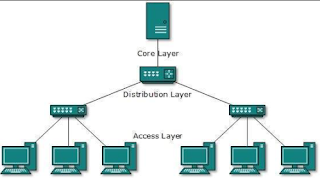
TREE
brunches, also known as Hierarchical Topology. this type of typologies is the most common form of network topology.
figure 6(tree topology)
+faster to send a message
+easy to set up other PC
-expensive to set up
-if the distribution layer is broken all the user cannot access the network.






Comments
Post a Comment